由我所18T5组与化物所肖春雷研究员、李杲研究员,以及荷兰代尔夫特工业大学化学工程系李冠娜博士合作的工作“Single-Atom Pt+ Derived from the Laser Dissociation of a Platinum Cluster: Insights into Nonoxidative Alkane Conversion”发表于Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters(J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2020, 11, 5987-5991),刘哲益博士为文章共同第一作者(https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.jpclett.0c01416)。
在该工作中,将193 nm紫外激光引入到Exactive EMR Orbitrap质谱系统的HCD解离阱中,对通过电喷雾进入质谱系统的有机配体保护的Pt团簇离子进行高效激光解离;发现在高能激光的作用下Pt团簇离子的外周配体发生完全脱离并且团簇核心完全分解,高效产生单原子Pt+离子。我们进一步将甲烷、乙烷、丙烷反应气体引入到HCD解离阱,与激光解离产生的Pt+离子实现原位吸附和催化活化反应,反应中间体和产物离子快速(10ms)转移到Orbitrap检测阱中实现高质量精度(<5ppm)鉴定分析。我们发现Pt+离子活化的甲烷转化通过Pt-CH2中间体与甲烷分子的交叉偶联产生[Pt+乙烷]+和[Pt+乙烯]+;而Pt+离子仅能促进乙烷和丙烷的非氧化脱氢,生成[Pt+烯烃]+和[Pt+炔烃]+。我们进一步通过密度泛函理论(DFT)计算对反应机理的细节进行了阐释。
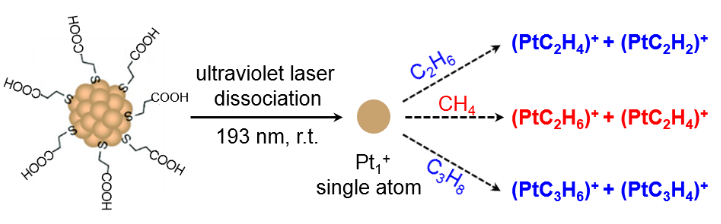
Schematic representation of single-atom Pt+ cations generated via 193 nm ultraviolet laser dissociation of the Pt clusters for “Pt+ + alkanes” conversion (e.g. methane, ethane and propane).
在本工作中我们提出了一种通过高能激光解离配体保护金属团簇高效产生单原子金属离子的全新策略,并通过与高分辨质谱的结合实现了金属离子催化活化烃类反应中间体和产物的快速检测定性。以上结果的取得证明我组搭建的高能紫外激光解离-高分辨质谱平台不仅在蛋白质序列、修饰分析方面有广泛的应用前景,在能源转化分析领域也是一种创新性的研究平台,目前相关后续工作正在持续推进。
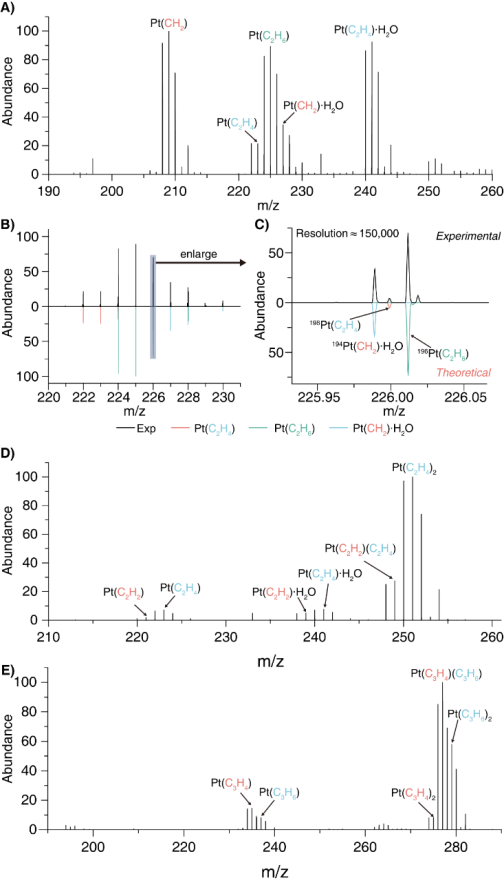
In-situ HRMS monitoring of the formed single-atom Pt+ cations in the presence of alkane gas, (a) methane ((b,c) the enlarged spectra of methane conversion intermediates), (d) ethane, (e) propane.